|
The purpose of EVA-Valuation is to measure the total
value added of a company´s operations, i.e.
the net cash generated in excess of claimholders´
return requirements.
This document describes EVA valuation in detail and in
our valuation model. If your would like to get an overview
of EVA valuation in general or practical examples (numerical
and graphical) about it, then
you should look at our EVA valuation tutorial.
The computation of EVA is closely related to DCF. Hence,
it starts with EBIT and ends with the fair value
of the share. The share price potential (which the
investors are interested in) is computed by comparing
the fair value with the current market price of
the share.
The basic formulation of EVA valuation is as follows:

|

|
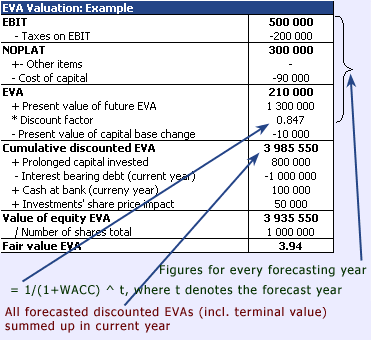
EVA is computed so that the "fair rate
of return to invested capital", i.e. WACC
times the invested capital, is subtracted from the
Net Operating Profit Less Added Tax (NOPLAT).
|
 |
Cumulative discounted EVA
is a yearly item in which all the forecast
years´ discounted EVAs are summed up. Hence,
the first item (current year) is the sum
of all forecast years´ EVAs at present value
terms.
|
 |
Value of equity EVA is divided by the number
of shares outstanding to get the fair value of
the company´s share.
|
More detailed formulation of Discounted EVA-valuation
is as follows:
 |
Other items include associated companies´
profit/loss (after tax), taxes on goodwill amortization,
minorities, extraordinary items and other income
statement adjustments.
|
 |
Cost of capital means the "fair rate
of return to invested capital", which goes
to all claimholders. It is computed by multiplying
Capital invested with WACC.
Capital invested is computed as follows:
- For all forecast years except terminal year:
Total equity + Interest bearing liabilities +
Convertibles - Total interest bearing financial
assets.
- For terminal year: (NOPLAT - Gross capital
expenditure - Change in working capital + Increase
in non-interest bearing liabilities - Total depreciation)
/ (Net sales growth * NOPLAT).
|
 |
Present value of future EVAs means the terminal
value of all EVAs, i.e. the approximation of EVAs
beyond the forecast horizon. It is computed as follows:
- Last forecast year´s EVA / (WACC
- Net sales growth rate).
|
 |
Present value of capital base change means
the discounted capital change in invested capital
after the last forecasted year:
- Capital base change = Capital invested
(terminal year) - Capital invested (last forecasted
year)
- Present value of capital base change =
Discount factor (last forecasted year) x Capital
base change
|
 |
Prolonged capital invested is the capital
invested (according to the beginning balance sheet)
that is prolonged to today. If as a discount factor
were used time at the end of the year (and thus
discount factor would always be integer), prolonging
would not be necessary here.
|
 |
Three items after Prolonged capital invested
are added so that DCF- and EVA-valuation would give
same result. (In DCF-valuation these items are added
so that the calculation gives the value of equity,
not value of firm.)
|
All items except for EBIT and Taxes on EBIT
the model calculates automatically. Thus, you can
freely change EBIT and Taxes on EBIT (and
naturally all the subitems which are blue).
See equations for the EVA-valuation
items.
|